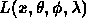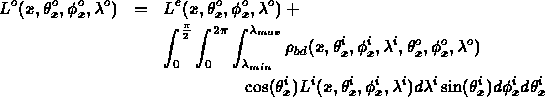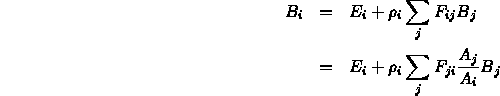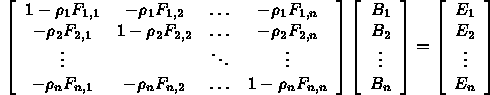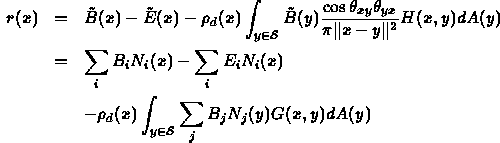- Ambient term is an approximation to diffuse interaction of light
- Would like a better model of this ambient light
- Idea: ``Discretize'' environment and determine interaction between each pair of pieces.
- Models ambient light under following assumptions:
- Conservation of energy in closed environment
- Only diffuse reflection of light
- All energy emitted or reflected accounted for by its reflection or absorption elsewhere
- All light interactions computed once, in a view
independent way
- Multiple views can then be rendered just using hidden surface removal
- No mirror/specular reflections
- Ideal for architectural walkthroughs
- at some point x
- in a specified direction
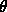 ,
, 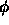
- per unit time
- per unit area perpendicular to the direction
- per unit solid angle
- for a specified wavelength
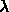
- denoted by